The Road Well Traveled: An Employee Perspective
The Road Well Traveled: An Employee Perspective Bridge House Advisors is super proud of our…

Welcome to the 5th installment of Bridge House Advisors’ Blog Series where we cover the “alphabet soup” of major standards, frameworks, and disclosure systems that affect and influence ESG and sustainability efforts for our clients. In this series, we will provide a basic overview of the standard or framework and the value it provides. We will also cover how Bridge House works with our clients in applying or supporting these frameworks into their ESG management programs. Lastly, we will cover any trends or pending changes that could impact how our clients apply these frameworks to their ESG and sustainability efforts.
Next Up…IFRS S2
What is IFRS S2 and Who is it for?
In November 2021, the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation launched the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) at the 26th U.N. Conference of the Parties (COP26) in Glasgow, Scotland. ISSB was created in an effort to drive convergence with other reporting requirements and promote efficiency for companies in navigating the overall ESG reporting landscape which is demonstrated in ISSB’s lineage in the graphic below:
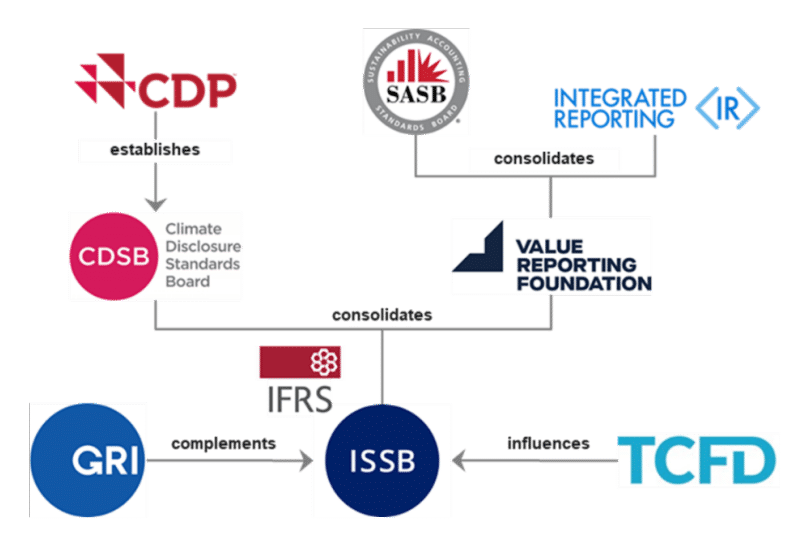
Two years after its formation, ISSB released the finalized versions of two new standards designed to be used in tandem:
These standards were developed to improve the alignment and interoperability of global ESG standards, reduce the reporting burden for preparers, and enhance the usefulness of sustainability disclosures for investors in making decisions. Furthermore, companies that adhere to these standards are required to provide sound data on sustainability and climate efforts which subsequently helps combat the challenges of corporate greenwashing.
Why is IFRS S2 important?
The IFRS S2 standard integrates the four core recommendations and 11 recommended disclosures included in the final report published by the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). The IFRS Foundation has now taken over the monitoring of companies’ progress on climate-related disclosures from the TCFD, and the TCFD has been disbanded.
The objective of IFRS S2 is to encourage companies to disclose information about climate-related risks and opportunities in order to provide investors and stakeholders with decision-useful, reliable, and comparable sustainability-related information when making investment decisions and comparing companies. Other frameworks and standards require memberships, signatories, surveys, etc.; however, compliance with IFRS S2 differs as it requires material climate-related information to be disclosed alongside financial statements so that stakeholders and investors can make informed decisions on the financial impact of climate change on the company.
Entities utilizing IFRS S2 can streamline their sustainability reporting processes while simultaneously enabling greater transparency of information, which may result in improved access to capital, governance, and strategies for companies.
Understanding a company’s climate-related risks and opportunities under IFRS S2 requires six key disclosures which are summarized below in Table 1.
Table 1: IFSR S2 Key Disclosures and Descriptions
Key Disclosure | Explanation |
Strategy and | The effects of climate-related risks and opportunities on a company’s strategy and decision-making. Requires an entity to disclose information about climate-related risks (physical and transition) and opportunities that could reasonably be expected to affect the entity’s cash flows, its access to finance, or cost of capital over the short, medium, or long term. |
Current and | The effects of climate-related risks and opportunities on a company’s current and anticipated financial performance, financial position, and cash flows. |
Climate | The resilience of a company’s strategy and business model to climate-related changes, developments, and uncertainties. Disclosures include climate resilience assessments, inputs, and key assumptions used in a scenario analysis. Transition plans that respond to the scenario analysis are also required. |
Scope 1-3 | Scope 1, 2, and 3 GHG emissions and their intensity per unit of economic or physical output. GHG accounting must be measured in accordance with the GHG Protocol. |
Industry-Specific Requirements | Industry-based metrics that are associated with one or more business models, activities, or other common features that characterize participation in an industry. The company shall leverage SASB’s industry-based metrics. |
Climate-Related | Includes both quantitative and qualitative climate-related targets the company has established in addition to targets the company is required to meet by law or regulation. |
Bridge House & IFRS S2
Beginning in 2025, investors will be able to evaluate a company’s climate-related risks and opportunities as reporting on IFRS S2 only recently started on 1 January 2024. Clients preparing to report to IFRS S2 should look no further as Bridge House is well positioned to assist in the reporting process. Bridge House has historically supported its clients in similar capacities by conducting Physical Climate Risk Assessments and Carbon Footprints, including Scopes 1, 2, and 3.
Combining a Physical Climate Risk Assessment with traditional due diligence strategies such as Phase I Environmental Site Assessments, Property Condition Assessments, and ESG Due Diligence Reviews can bolster the process by identifying urgent findings at individual sites or collectively for seemingly low-risk assets clustered in vulnerable areas. Furthermore, Bridge House has performed qualitative transitional risk analyses to evaluate how the shift to a low-carbon economy can impact a company. This transitional risk analysis often creates a blueprint for a company to successfully navigate into a lower carbon economy protecting or even gaining market share along the way.
As regulatory and market pressure continues to drive companies to quantify their GHG emissions, Bridge House is well-equipped to support with boundary scoping, data collection, and GHG calculations. Climate-related opportunities can be determined during the GHG accounting process as an analysis of major direct emission sources can identify potential reduction opportunities. Similarly, indirect emission sources such as electricity consumption can be investigated to identify no cost and low-cost operational improvements that can effectively decrease carbon emissions while simultaneously reducing operating costs.
Looking Ahead
A suite of Environmental Compliance, Health and Safety, Liability Management, Sustainability, and Climate Change service offerings, combined with an eclectic group of passionate professionals, positions Bridge House as a trusted partner to support clients in IFRS S2 reporting.
To learn more about IFRS S2, how it can influence your ESG program, or to baseline or improve your reporting performance, contact one of our IFRS S2 Frameworks leads below.

Bryan Rodriguez
brodiguez@bridgehouseadvisors.com
LinkedIn

Sarah Arnberger, P.E.
sarah@bridgehouseadvisors.com
LinkedIn

Christian Fioretti
cfioretti@bridgehouseadvisors.com
LinkedIn
The Road Well Traveled: An Employee Perspective Bridge House Advisors is super proud of our…
One Year at Bridge House: An Employee Perspective Bridge House Advisors is super proud of…
2023 Bridge House Advisors CEO Interview – Christer Setterdahl Welcome to the launch of Bridge…
